Key Dates
-
categories
-
Architecture
-
Interior Design
-
Space Plus
Space Design
-
Product Design
-
Communication Design
-
Advertising & Marketing
-
Service & System Design
Experience Design
-
Digital Innovation
-
Web & App Design
-
Better Future
Transformative Design
-
- winners
- best of the best
3D Printed Corneas
Newcastle University | Product Design - Medical
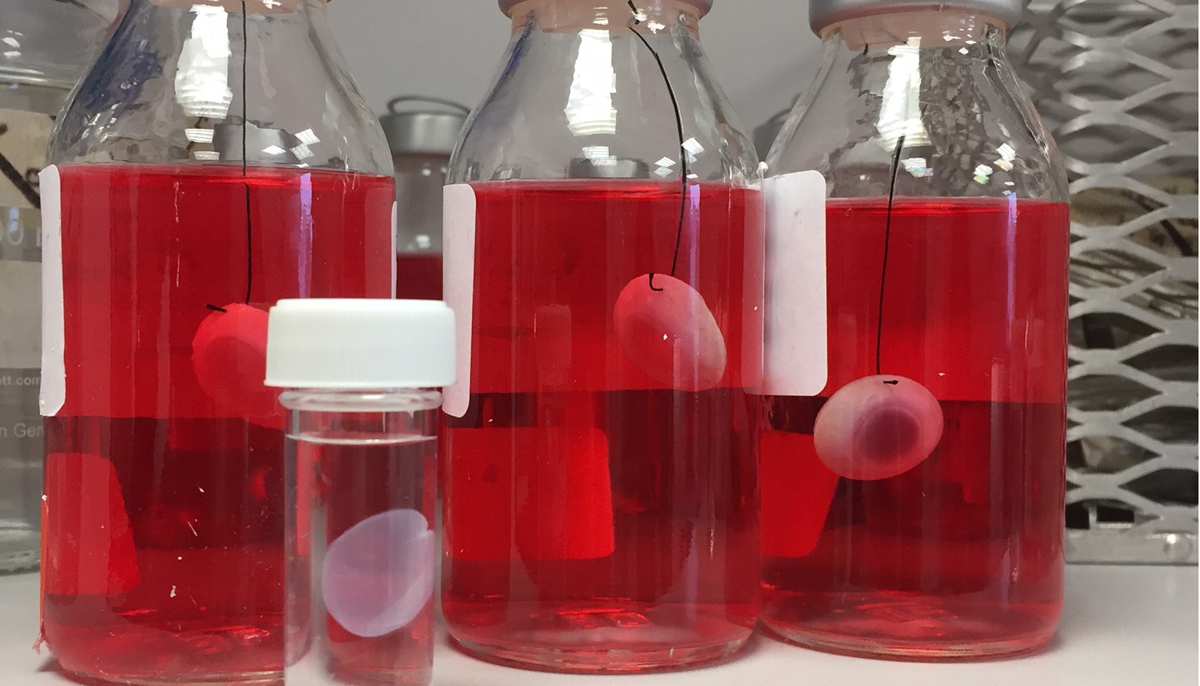
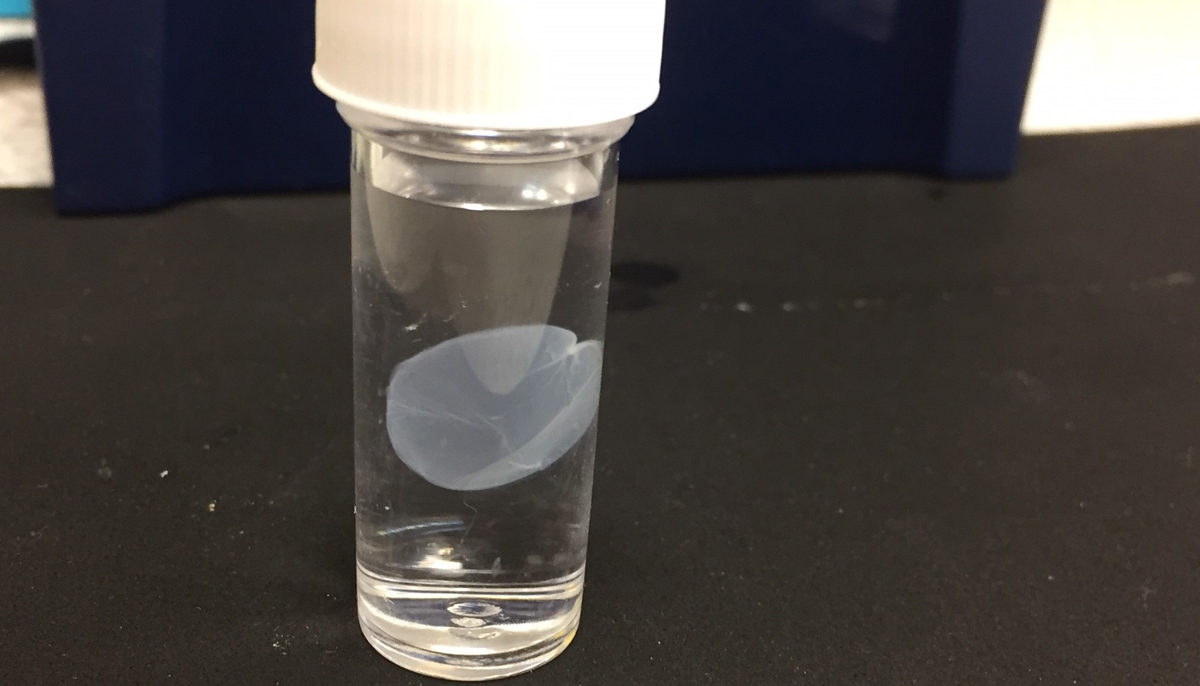
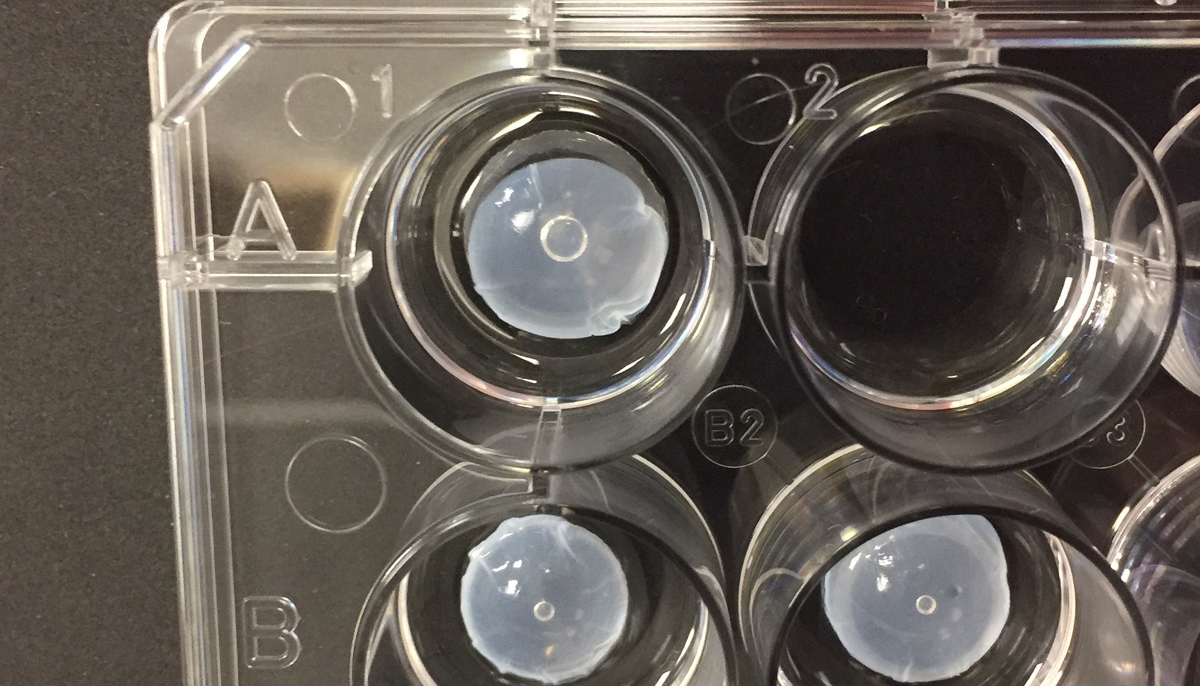




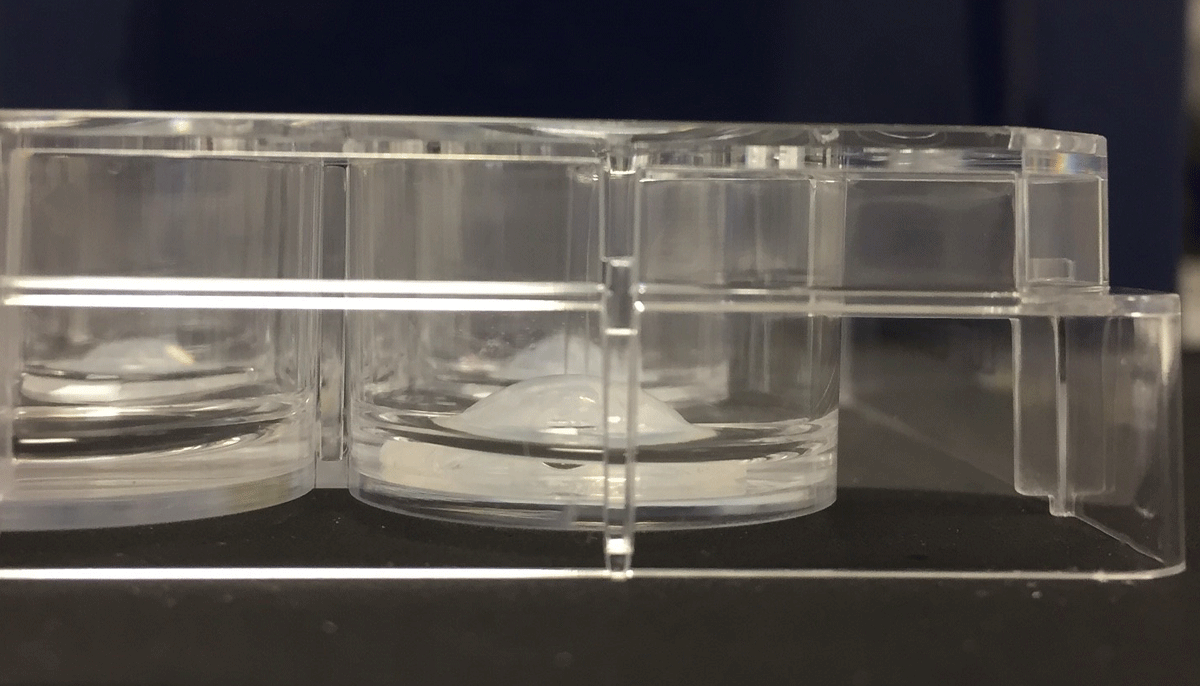

Image Credit : Newcastle University

Project Overview
The first human corneas have been 3D printed by scientists at Newcastle University.
It means the technique could be used in the future to ensure an unlimited supply of corneas.
Organisation
Team
Professor Che Connon Dr Steve Swioklo Ms Abigail Isaacson
Project Brief
As the outermost layer of the human eye, the cornea has an important role in focusing vision.
Yet there is a significant shortage of corneas available to transplant, with 10 million people worldwide requiring surgery to prevent corneal blindness as a result of diseases such as trachoma, an infectious eye disorder.
In addition, almost 5 million people suffer total blindness due to corneal scarring caused by burns, lacerations, abrasion or disease.
Project Innovation/Need
Using a simple low-cost 3D bio-printer, the bio-ink was successfully extruded in concentric circles to form the shape of a human cornea. It took less than 10 minutes to print.
The stem cells were then shown to culture – or grow.
The scientists, including first author Ms Abigail Isaacson from the Institute of Genetic Medicine, Newcastle University, also demonstrated that they could build a cornea to match a patient’s unique specifications.
The dimensions of the printed tissue were originally taken from an actual cornea. By scanning a patient’s eye, they could use the data to rapidly print a cornea which matched the size and shape.
Product Design - Medical
This award celebrates creative and innovative design for either a component or overall product. Consideration given to aspects that relate to human usage, aesthetics, selection of components and materials, and the resolution of assembly, manufacturing and the overall function.
More Details

